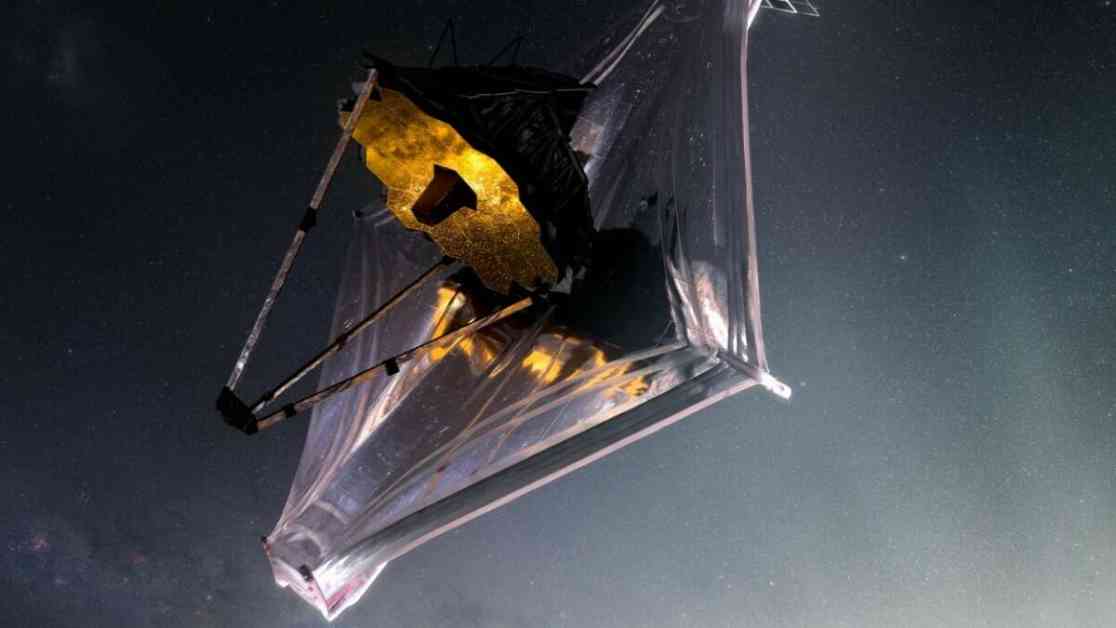
The James Webb Space Telescope recently captured an image of a massive exoplanet in a remote solar system. The exoplanet, named Epsilon Indi Ab, is located 12 light-years away from Earth. This gas giant planet is similar to Jupiter but twice as massive. The planet’s temperature is around 35 degrees Fahrenheit, making it one of the coldest planets ever directly imaged.
The Webb telescope used a coronagraph to capture the faint light from this distant planet. This advanced telescope is the most powerful space observatory ever built, with a mirror over 21 feet across, allowing it to capture more light and see more distant and ancient objects in the universe. Unlike the Hubble Space Telescope, Webb primarily focuses on viewing light in the infrared spectrum, which enables it to penetrate cosmic clouds and reveal new insights about the early universe.
One of the remarkable features of the Webb telescope is its ability to study exoplanets in our galaxy. Equipped with specialized spectrographs, the telescope can decipher the molecules present in the atmospheres of distant exoplanets, including gas giants and rocky worlds. This technology opens up new possibilities for discovering unknown phenomena and expanding our understanding of the universe.
Astronomers are excited about the potential of the Webb telescope to provide groundbreaking insights into the cosmos. By studying planets like Epsilon Indi Ab, scientists can gather valuable data about the composition and properties of these distant worlds. The discoveries made by the Webb telescope could revolutionize our understanding of exoplanets and pave the way for new discoveries in the field of astronomy.
In conclusion, the James Webb Space Telescope’s recent image of the exoplanet Epsilon Indi Ab showcases the incredible capabilities of this advanced observatory. With its powerful mirror, infrared view, and spectrographic instruments, the Webb telescope is poised to unveil new secrets of the universe and expand our knowledge of distant planets and solar systems. Stay tuned for more exciting discoveries from this groundbreaking telescope.