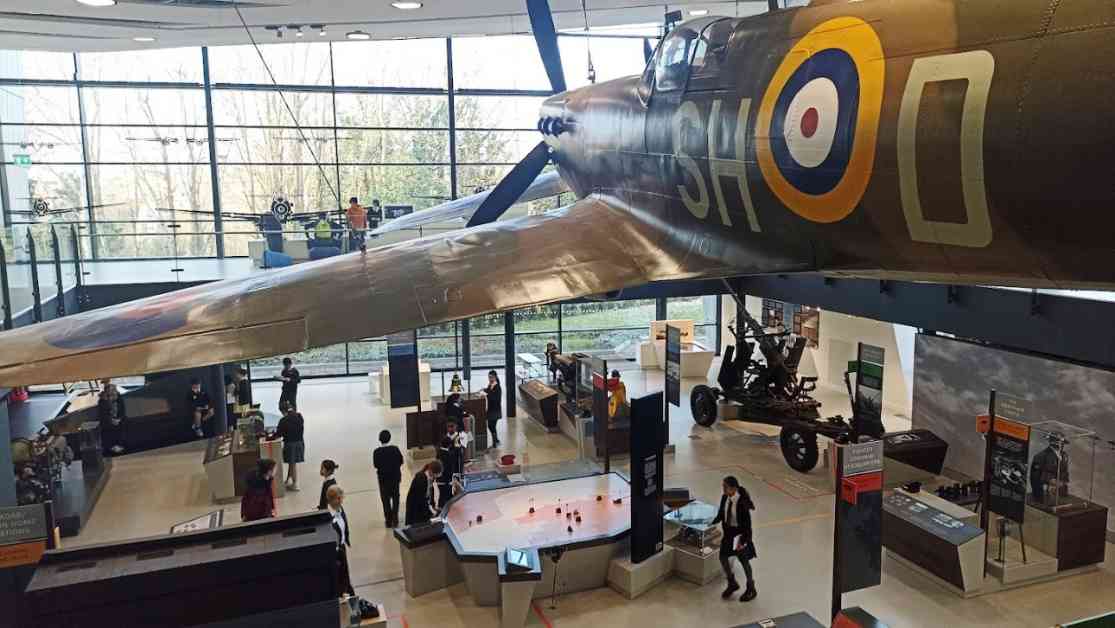
The Battle of Britain Bunker in Uxbridge was a key strategic location during World War II, as recent archaeological work has revealed. The bunker, which is 60 feet below ground and was constructed in 1938, played a vital role in coordinating Britain’s response to Luftwaffe attacks.
One interesting discovery from the archaeological research is that the bunker was camouflaged as a decorative garden during the war. This clever disguise made it appear as part of a designed landscape from the air, helping to protect it from enemy attacks. Despite the lack of wartime photographs showing the bunker above ground, historic aerial images suggest that it blended in with the nearby Hillingdon House.
In addition to its camouflage, the bunker had multiple defences in place to protect it from both aerial and ground attacks. Gun pits, brick pillboxes, and barbed wire entanglements were all part of the defensive measures taken to safeguard the command centre. The extensive use of earth and concrete to shield the bunker from direct hits further highlights the lengths to which the RAF went to protect this strategic location.
One intriguing discovery from the archaeological research is the presence of a Campaign for Nuclear Disarmament (CND) symbol scratched on a pillbox at the site. This symbol serves as evidence of later peaceful protests that took place on the grounds of the bunker.
Sandy Kidd, an archaeologist at Historic England, noted that the layered defences found at the bunker reflect the fear of the command centre being compromised. The ongoing conservation work and repairs at the site have allowed for further archaeological research, unveiling more secrets from this historic location.
Today, the Battle of Britain Bunker serves as a popular attraction and education centre managed by Hillingdon Council. It stands as a testament to the bravery and ingenuity of those who defended Britain during one of its darkest hours. The bunker’s hidden history continues to fascinate visitors and researchers alike, shedding light on the innovative tactics used to protect this crucial wartime asset.