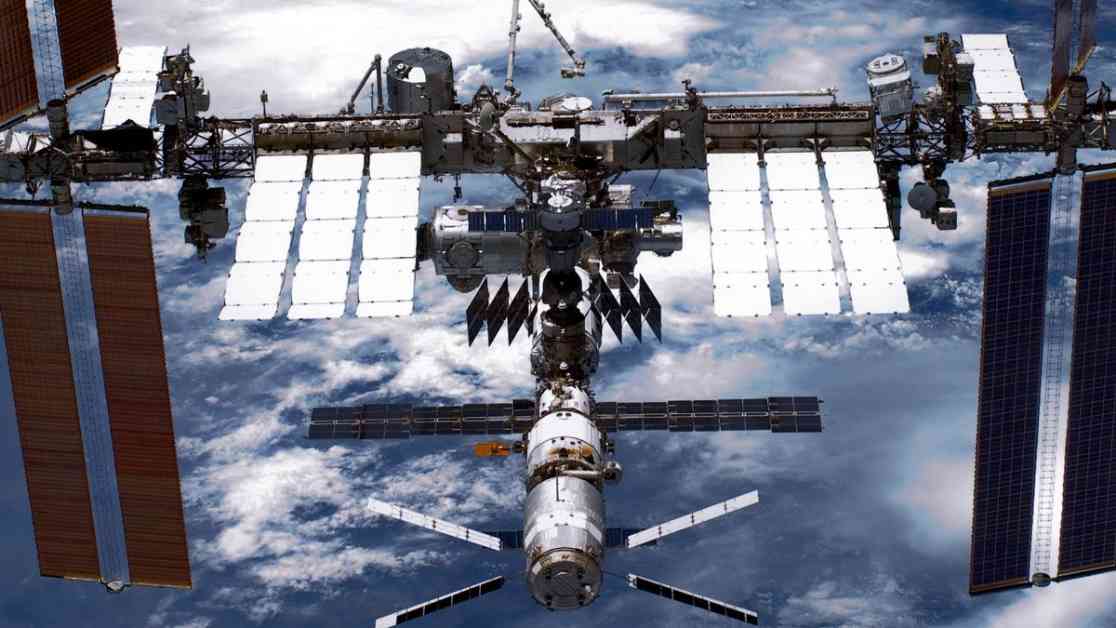
The detection of antimatter particles on the International Space Station (ISS) has sparked new research and theories in the field of physics. Scientists have found evidence of antihelium nuclei, which may have been produced by cosmic fireballs, challenging the current Standard Model of Physics. This discovery could potentially lead to a better understanding of unknown physics and the formation of the universe.
The Standard Model predicts that all elementary particles have corresponding antiparticles with opposite electric charges, which would have annihilated each other after the Big Bang. However, antimatter in the universe is rare and transient, raising questions about its origins. While particle accelerators can generate antiparticles, the detection of antihelium nuclei on the ISS suggests a new source for these particles.
The Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer (AMS-02) detected around 10 antihelium nuclei, consisting of antiprotons and antineutrons, which do not align with the predictions of the Standard Model. This discrepancy has led scientists to explore the possibility of cosmic fireballs, dense regions of space containing large numbers of antiparticles, as a potential source of these particles.
The recent study published in the journal Physical Review D proposes that fireballs could be formed from the collision of dense clumps of dark matter, a mysterious substance that makes up a large portion of the universe. These fireballs could release antiprotons, antineutrons, and antihelium nuclei into space, which may eventually reach Earth and be detected.
Further research and validation are needed to confirm this hypothesis. The General AntiParticle Spectrometer (GAPS) project, launching a balloon over Antarctica later this year to detect antimatter cosmic rays, could provide additional insights into the origins of antihelium nuclei. Scientists are eagerly awaiting the results of ongoing studies to shed light on this intriguing puzzle in particle physics.
Andrey, a science writer specializing in physics, space, and technology, highlights the importance of these discoveries. With a background in elementary particle physics and string theory, Andrey’s articles have been published in various scientific publications, emphasizing the significance of antimatter research in advancing our understanding of the universe.